Exploring Interior Design Styles: From Traditional Elegance to Contemporary Chic
August 20, 2023
The Golden Age of Interior Design: The Renaissance
August 21, 2023The Modernism Movement: Unpacking Art Deco and Bauhaus Influences

The modernism movement, a revolutionary wave that shook the artistic and architectural world in the early 20th century, was a rebellion against traditional design norms. Two of its most significant schools of thought, “Art Deco and Bauhaus,” have left an indelible mark on contemporary design. This article unpacks these distinctive styles, exploring their origins, key features and enduring influence on modern aesthetics.
Table of Contents
Defining Art Deco: Style and Characteristics
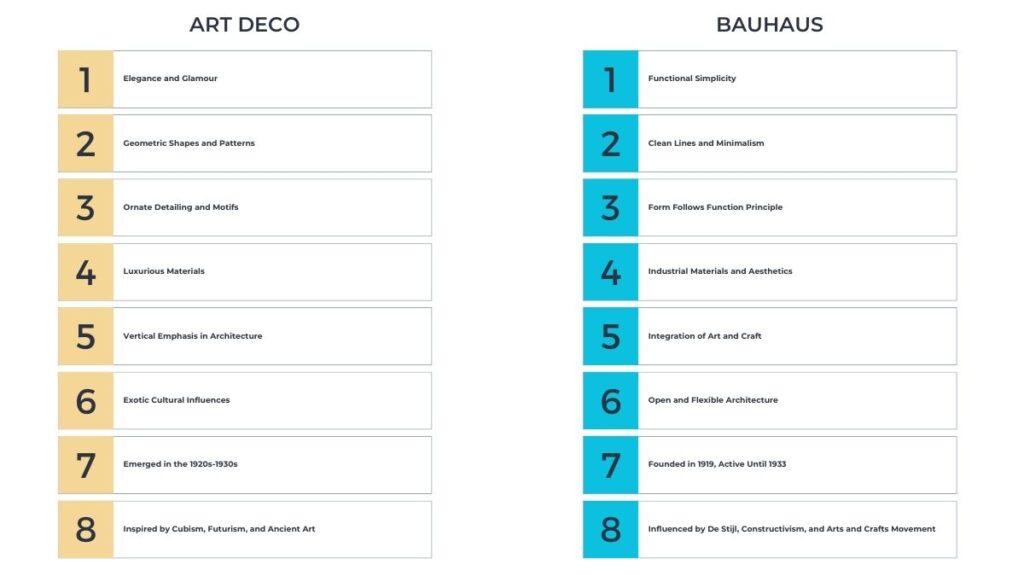
Art Deco emerged in the 1920s, celebrating luxury, glamour, and exuberance. Characterized by rich colors, bold geometric shapes, and lavish ornamentation, it reflected the optimism and rapid industrialization of the Roaring Twenties. This style, though initially popular in architecture and interior design, extended to fashion, jewelry, cars, and everyday objects, making Art Deco a truly comprehensive design language.

Unpacking Bauhaus: Principles and Design Aesthetics
In stark contrast to the ornate Art Deco, Bauhaus, originating in Germany in 1919, advocated simplicity, functionality and rationality. The school’s ethos, encapsulated in its maxim “form follows function,” believed in the harmonious existence of design and industrial production. Its minimalist aesthetics, with an emphasis on straight lines and primary colors, went on to influence multiple design fields, from typography to architecture.

Art Deco and Bauhaus: The Intersecting Threads
Art Deco and Bauhaus, despite their apparent dissimilarities, share common roots in the modernism movement. They both embraced modern materials, like steel and glass, and reflected a breakaway from historical revival styles. Moreover, both sought to integrate art and industry, albeit in their unique ways.
Exploring the Historical Context of Art Deco and Bauhaus
The Roaring Twenties and Art Deco
Art Deco flourished in the prosperous post-World War I era, an epoch of optimism and novelty. This “Jazz Age” aesthetic, with its flamboyant motifs and gleaming surfaces, embodied the dynamism and opulence of the period. From New York’s Chrysler Building to Shanghai’s Park Hotel, Art Deco became synonymous with progress and luxury.
Bauhaus and the Inter-War Years
Conversely, Bauhaus arose amidst the socio-political upheaval of inter-war Germany. Its stripped-down aesthetic and functional focus were reflections of the era’s practicality and desire for societal reform. The school’s radical approach to design education, merging fine art, crafts and technology, was seen as a means to rebuild a war-ravaged society.
Key Figures in Art Deco and Bauhaus
Influential Art Deco Designers
Designers like Eileen Gray and Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann played pivotal roles in shaping Art Deco aesthetics. Gray’s luxurious lacquer work and Ruhlmann’s high-end furniture elevated Art Deco to the epitome of chic, reflecting the era’s fascination with craftsmanship and exotic materials.
Pioneers of Bauhaus
Bauhaus owes its groundbreaking approach to masters like Walter Gropius, its founder, and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, its last director. Their architectural designs, guided by the principles of clarity, simplicity, and functionality, laid the groundwork for modernist architecture. Artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Paul Klee, who taught at the Bauhaus, also played a crucial role in establishing its aesthetic.
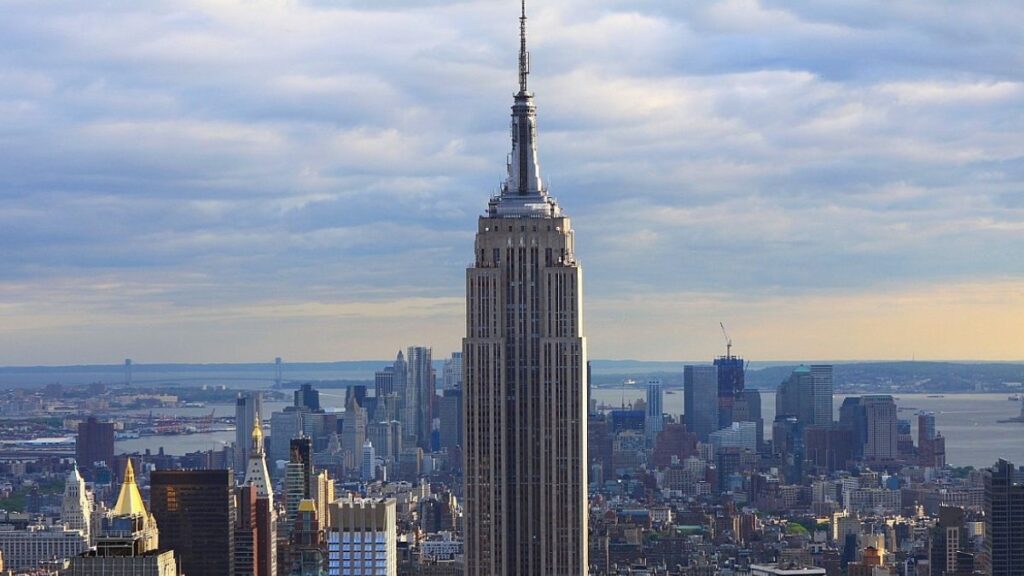
Art Deco in Architecture
Art Deco’s architectural legacy is evident in numerous skylines worldwide. The style, favoring symmetry and geometric forms, often incorporated elements like sunbursts, chevrons, and zigzags. Iconic Art Deco structures include the Chrysler Building in New York, the Hoover Building in London, and the Palais de Tokyo in Paris.
Bauhaus and its Architectural Triumphs
Bauhaus architecture, characterized by its flat roofs, smooth facades, and open floor plans, set the tone for modern design. Structures like the Dessau Bauhaus Building and the Villa Tugendhat by Mies van der Rohe showcase the style’s innovative use of glass and steel, emphasizing the school’s focus on functionalism and industrial materials.

Art Deco and Bauhaus Influence on Furniture Design
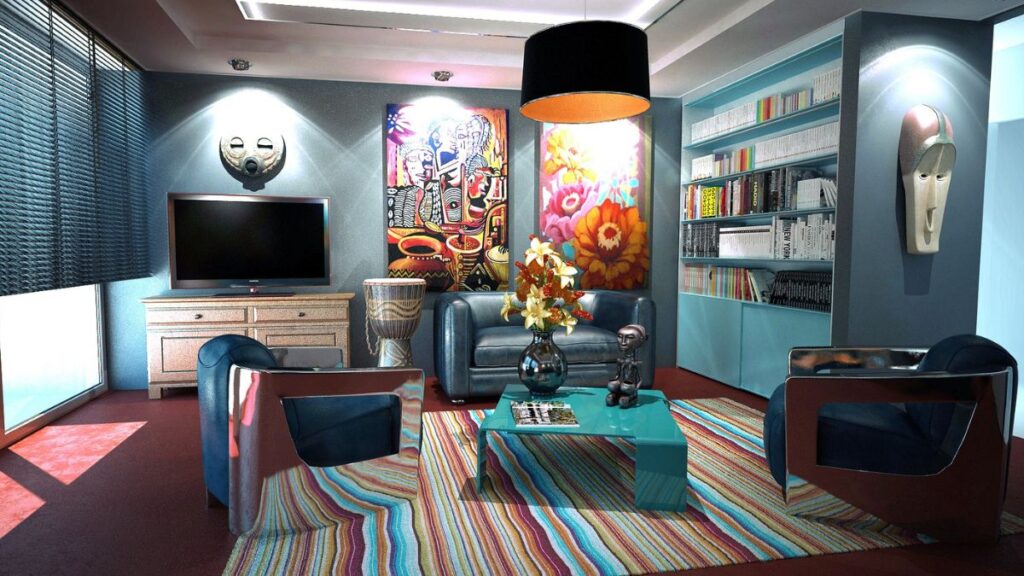
The Luxurious Allure of Art Deco Furniture
Art Deco furniture, known for its ornate details and luxurious materials, radiated glamour. Designers utilized rich woods like mahogany and ebony, pairing them with shiny metals and extravagant inlays. The style’s geometric patterns, curving lines, and bold colors reflected a sense of exuberance and elegance.
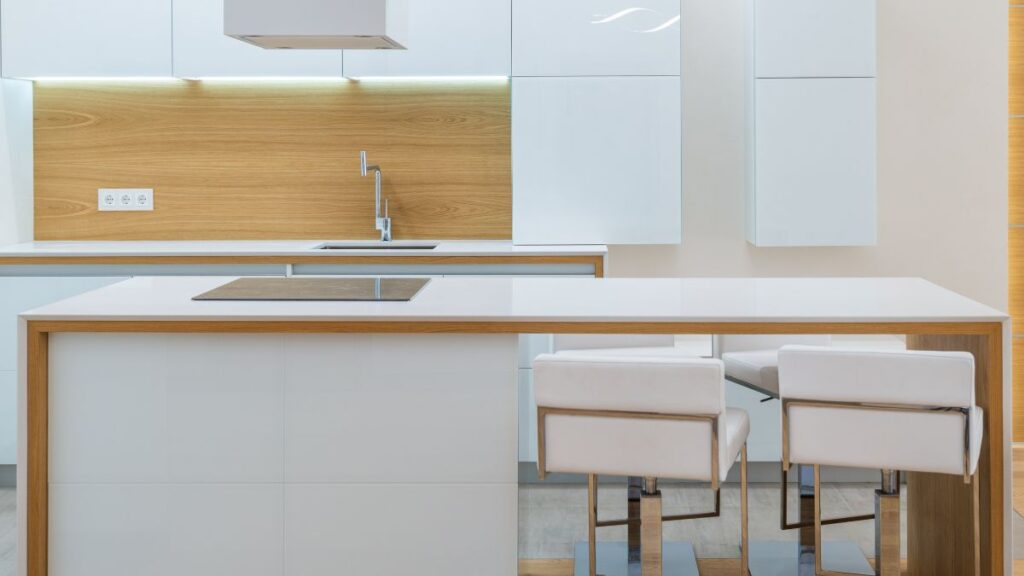
The Functional Aesthetic of Bauhaus Furniture
Bauhaus furniture, on the other hand, placed a heavy emphasis on functionality and simplicity. Designers used new industrial materials, like tubular steel, in innovative ways. Pieces such as Marcel Breuer’s Wassily Chair and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe’s Barcelona Chair became emblematic of the movement’s minimalist, functional approach.
Art Deco and Bauhaus Today: A Lasting Influence
Art Deco’s Enduring Appeal
Today, Art Deco continues to inspire designers with its bold and luxurious aesthetic. From fashion to furniture, its influence is undeniable. The style’s association with glamour and luxury also makes it a popular choice for high-end hotels and restaurants.

Bauhaus: The Foundation of Modern Design
Bauhaus’s influence on modern design is immeasurable. The movement’s philosophy of form follows function continues to guide design education and practice. Bauhaus’s clean lines and minimalistic aesthetic remain staples of contemporary design, from architecture to graphic design and typography.
Key Takeaways: Art Deco and Bauhaus Influences on Modern Design
Art Deco and Bauhaus, two pivotal movements within modernism, have left enduring legacies that shape contemporary design aesthetics. Art Deco’s lavish, geometric elegance and Bauhaus’s functional, minimalist ethos both reflect the innovative spirit of their time. Despite their differences, both styles share commonalities in their embrace of modern materials and their break from historical revival styles. Today, these influences are visible across architecture, interior design, furniture, and beyond, demonstrating the timeless appeal and adaptability of their principles.
Conclusion
The Modernism Movement, with Art Deco and Bauhaus as two of its most significant chapters, had a profound impact on shaping the aesthetics of the 20th century and beyond. From the opulent grandeur of Art Deco to the minimalist functionality of Bauhaus, their influences permeate all design aspects today. As we appreciate these historical design movements, we also anticipate how their timeless principles will continue to guide the future of design.

FAQs
1. Who were some key figures in the Art Deco movement?
Influential designers in the Art Deco movement included Eileen Gray and Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann. Their work, characterized by luxurious materials and intricate craftsmanship, helped define the chic and elegant aesthetic of Art Deco.
2. What is the main difference between Art Deco and Bauhaus?
Art Deco is characterized by its lavishness, ornate details, and luxurious materials, reflecting the era’s glamour and optimism. On the other hand, Bauhaus is recognized for its functionality, simplicity, and use of industrial materials, mirroring the era’s desire for practicality and societal reform.
3. Can Art Deco and Bauhaus design coexist in the same space?
While they are fundamentally different, Art Deco and Bauhaus elements can coexist in a space with a careful and thoughtful design approach. Balancing the opulence of Art Deco with the minimalist aesthetics of Bauhaus could create a unique and balanced space.
4. How does Bauhaus influence modern design?
The influence of Bauhaus on modern design is profound. Its “form follows function” philosophy, emphasis on simplicity, and innovative use of industrial materials are foundational to contemporary design aesthetics and principles.
5. Where can I see examples of Art Deco and Bauhaus architecture?
Art Deco architecture can be seen in buildings like the Chrysler Building in New York and the Palais de Tokyo in Paris. Examples of Bauhaus architecture include the Dessau Bauhaus Building in Germany and Villa Tugendhat in the Czech Republic.
6. Are Art Deco and Bauhaus still popular in interior design today?
Yes, both Art Deco and Bauhaus continue to inspire interior design today. Art Deco’s luxurious aesthetics often find their way into high-end settings, while Bauhaus’s functional and minimalist approach remains a popular choice for contemporary designs.
7. What defines Art Deco style?
Art Deco is defined by its emphasis on luxury, glamour, and exuberance. It features rich colors, bold geometric shapes, and lavish ornamentation. This style was prevalent in various fields such as architecture, interior design, fashion, and even everyday objects during the 1920s.
8. What are the core principles of Bauhaus design?
Bauhaus design is centered around simplicity, functionality, and rationality. The school’s motto, “form follows function,” reflects its belief in the harmonious existence of design and industrial production. It uses minimalistic aesthetics with straight lines and primary colors.
9. How did the historical contexts of Art Deco and Bauhaus influence their styles?
Art Deco emerged during the prosperous post-World War I era, embodying the optimism and dynamism of the Roaring Twenties. Bauhaus arose in inter-war Germany, reflecting the socio-political upheaval of the time with a focus on practicality and societal reform.
10. What were the contributions of Bauhaus pioneers to modern design?
Walter Gropius and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe were instrumental in Bauhaus’s development, emphasizing clarity, simplicity, and functionality in architecture. Artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Paul Klee also significantly influenced Bauhaus aesthetics through their teachings.
11. What are some iconic examples of Art Deco architecture?
Iconic Art Deco structures include the Chrysler Building in New York, the Hoover Building in London, and the Palais de Tokyo in Paris. These buildings are known for their geometric forms, symmetry, and decorative elements like sunbursts and zigzags.
12. How does Bauhaus architecture differ from Art Deco?
Bauhaus architecture is characterized by flat roofs, smooth facades, and open floor plans, focusing on functionalism and industrial materials like glass and steel. In contrast, Art Deco emphasizes ornamental details and luxurious materials.
13. How have Art Deco and Bauhaus influenced modern furniture design?
Art Deco furniture is known for its ornate details and use of luxurious materials, such as rich woods and shiny metals. Bauhaus furniture emphasizes functionality and simplicity, utilizing industrial materials like tubular steel in innovative ways.
14. Are there any modern spaces that blend Art Deco and Bauhaus styles?
Yes, contemporary designers often blend the opulence of Art Deco with the minimalist aesthetics of Bauhaus to create unique and balanced spaces. This fusion can result in visually striking environments that offer both luxury and practicality.
15. What is the lasting impact of Art Deco and Bauhaus on contemporary design?
Art Deco’s bold and luxurious aesthetic continues to inspire fashion, furniture, and interior design, particularly in high-end settings. Bauhaus’s principles of simplicity and functionality remain foundational in modern design education and practice, influencing architecture, graphic design, and typography.

