Unraveling the Role of Computer-Aided Design in Interior Design
July 15, 2023
Introduction to Legal Considerations in Interior Design
July 17, 2023Color Theory in Interior Design: Creating Mood with Color

The power of color to transform a room is nothing short of magical. Through color, we can set the mood of a space, tell a story, and create harmony within different design elements. Understanding “Color Theory in Interior Design” is essential for anyone looking to make deliberate, effective choices in their home decor.
Table of Contents
Understanding Color Theory
Color theory is a framework that designers use to understand how colors relate to each other. At the heart of color theory is the color wheel, a visual representation of the colors and how they blend and contrast.
The Color Wheel
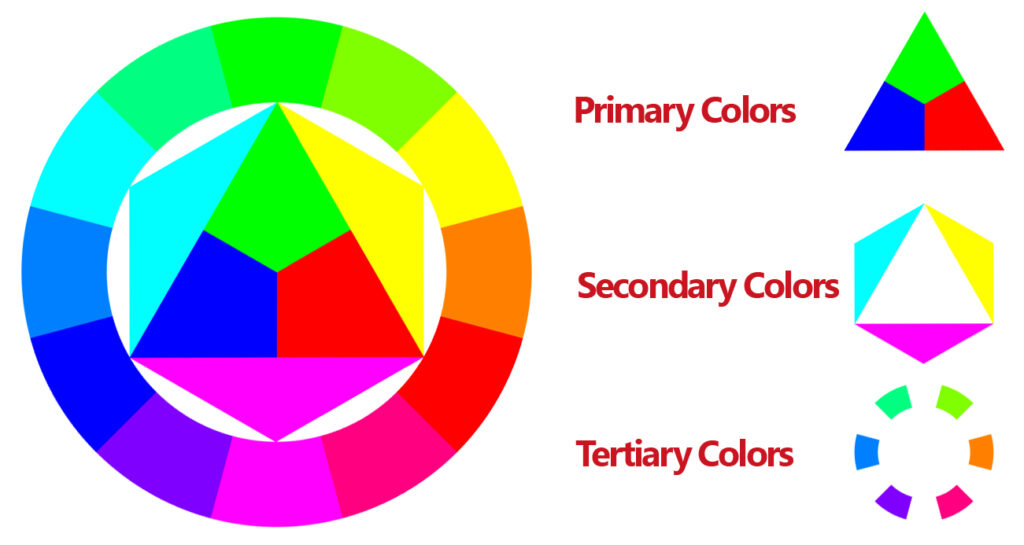
The color wheel is a circular diagram of colors arranged by their chromatic relationship. The wheel includes primary colors (red, blue, yellow), secondary colors (green, orange, purple), and tertiary colors (mixtures of primary and secondary colors).
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Colors
Primary colors are the three pigment colors that cannot be formed by any combination of other colors. All other colors are derived from these three hues. Secondary colors are created by mixing primary colors. Tertiary colors are made by combining a primary color with a secondary color.
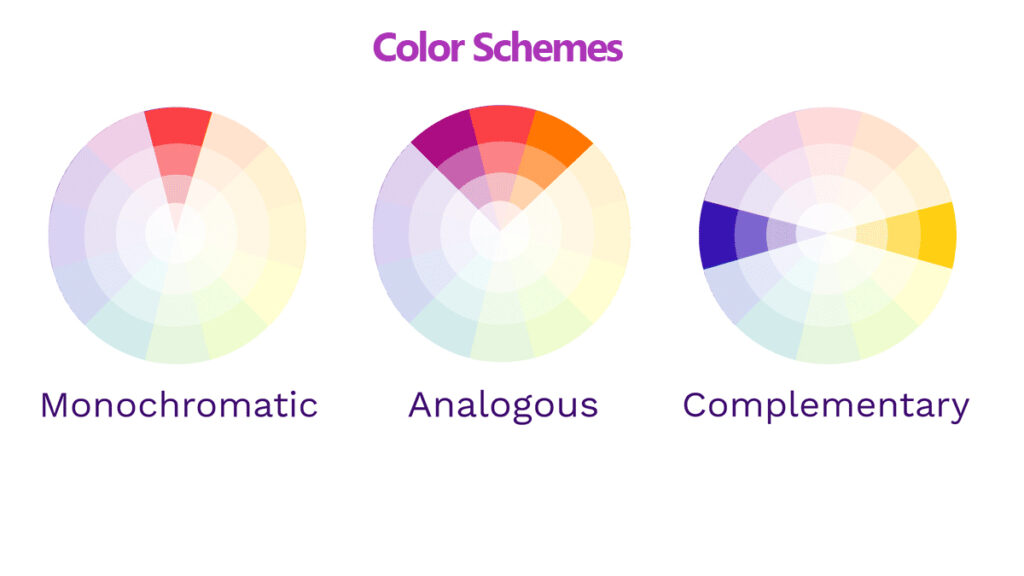
Complementary, Analogous, and Monochromatic Color Schemes
These are three basic color schemes in color theory. Complementary colors are opposite each other on the color wheel and create vibrant contrasts. Analogous colors are next to each other on the wheel and provide a harmonious look. Monochromatic schemes involve variations in lightness and saturation of a single color.
The Psychology of Colors
Colors evoke emotions and affect our mood. Understanding the psychology of color can help us make purposeful design choices.
Warm Colors
Colors like red, orange, and yellow are considered warm colors. They evoke emotions ranging from feelings of warmth and comfort to feelings of anger and hostility.
Cool Colors
Cool colors, such as blue, green, and purple, elicit feelings of calm and relaxation but can also evoke feelings of sadness.
Neutral Colors
Neutral colors, such as white, gray, and brown, provide a balancing backdrop for other colors and help to create a calming and sophisticated atmosphere.
Applying Color Theory in Interior Design
Once you understand color theory, you can apply it to your interior design decisions.

Choosing a Color Palette
Choosing a color palette is the first step. Depending on the mood you want to create, you might choose a palette based on analogous colors for a harmonious feel, or complementary colors for a bold, dramatic look.
Using Colors to Create Mood and Atmosphere
Consider the mood you want to evoke. For example, blues and greens might be used to create a calm, serene bedroom, while yellows and oranges might be chosen to create a lively, social atmosphere in a living room.
Playing with Color Proportions
When applying your color palette, consider the proportion of each color. The 60-30-10 rule is a well-known design principle. This rule suggests that 60% of the room should be the dominant color, 30% a secondary color, and 10% an accent color.

Tips and Tricks for Using Color Theory
Understanding color theory and how it influences interior design can make your decorating process more intuitive and fun. Here are some tips to get you started:
- Always consider the mood you want to create before choosing a color palette.
- Use the color wheel to help you understand how different colors interact.
- Don’t be afraid to play with different color combinations and schemes.
- Remember the importance of balance and harmony when applying colors.
Key Takeaways: Harnessing the Power of Color Theory in Interior Design
Understanding color theory allows designers to select hues that set the desired mood and tell a story in a space. Primary, secondary, and tertiary colors form a framework, while complementary, analogous, and monochromatic schemes offer versatile design options. Balancing warm, cool, and neutral tones effectively through proportions like the 60-30-10 rule creates visually compelling and harmonious interiors.
Conclusion
Color theory is a powerful tool in interior design, helping to create spaces that reflect your personality and evoke the desired mood. Whether you’re looking to create a calming sanctuary, a vibrant social space, or anything in between, understanding and applying color theory can help you achieve your design goals.
FAQs
1. How do complementary and analogous color schemes differ?
Complementary schemes utilize colors directly opposite each other on the color wheel, creating a bold contrast that draws attention. Analogous schemes use colors next to each other on the wheel, resulting in a harmonious and cohesive appearance.
2. What is color theory in interior design?
Color theory in interior design is a framework that designers use to understand how colors relate to each other and how they can influence our emotions and behaviors.
3. What are the primary, secondary, and tertiary colors?
Primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. Secondary colors (green, orange, purple) are created by mixing primary colors. Tertiary colors are made by combining a primary color with a secondary color.
4. What are the different color schemes in color theory?
The basic color schemes in color theory are complementary, analogous, and monochromatic. Complementary colors are opposite each other on the color wheel, analogous colors are next to each other, and monochromatic schemes involve variations in lightness and saturation of a single color.
5. How can I apply color theory in my home?
Once you understand color theory, you can choose a color palette, use colors to create mood and atmosphere, and play with color proportions.
6. What is the psychology of color in interior design?
The psychology of color refers to how colors can influence our emotions and behaviors. For example, warm colors can evoke feelings of warmth and comfort but also feelings of anger and hostility, while cool colors can elicit feelings of calm and relaxation but also feelings of sadness.
7. What is the importance of color theory in interior design?
Color theory serves as a guiding framework for designers to understand the relationships between colors and how they influence emotions and behavior. By mastering these principles, designers can create cohesive and impactful designs that set the desired mood.
8. How are primary, secondary, and tertiary colors defined?
Primary colors are red, blue, and yellow, which cannot be created by mixing other colors. Secondary colors are green, orange, and purple, formed by mixing primary colors. Tertiary colors are combinations of primary and secondary colors, resulting in hues like red-orange or blue-green.
9. What are the different types of color schemes used in interior design?
Complementary, analogous, and monochromatic are the primary color schemes in interior design. Complementary schemes use colors opposite each other on the wheel for striking contrast. Analogous schemes include colors adjacent to each other, offering harmonious blends, while monochromatic schemes focus on varying shades and tones of a single color.
10. How do warm and cool colors affect the mood of a room?
Warm colors, like red, orange, and yellow, evoke warmth, energy, and excitement but can also convey intensity or hostility. Cool colors, such as blue, green, and purple, bring a calming, relaxed vibe but may also suggest sadness.
11. What role do neutral colors play in interior design?
Neutral colors, including white, gray, and brown, provide a balancing backdrop that can either highlight accent colors or create a sophisticated, calming atmosphere. They offer great flexibility in pairing with bolder hues.
12. How does the 60-30-10 rule help designers apply color schemes effectively?
The 60-30-10 rule suggests using a dominant color for 60% of the space, a secondary color for 30%, and an accent color for 10%. This principle ensures a balanced color distribution, creating visual harmony and guiding the eye effectively.
13. How can homeowners choose a color palette to set the right mood in their space?
Choosing a color palette depends on the desired mood. For instance, blue and green palettes create a serene environment for bedrooms, while oranges and yellows foster a lively atmosphere in social spaces. The chosen color scheme should align with the room’s purpose.
14. What steps should I take when experimenting with new color schemes?
Start by considering the mood you want to achieve and refer to the color wheel to understand color relationships. Experiment with different combinations using paint samples or digital tools to visualize the outcome. Ensure balance by following the 60-30-10 rule or other proportion principles.
15. What is the psychology of color and how does it influence design?
The psychology of color examines how different hues affect emotions and behavior. For instance, warm colors may promote energy or tension, while cool colors induce relaxation. Understanding these effects helps designers use color strategically to influence the mood of a space.
Master the art of proportion and scale in interior design with our insightful article, Understanding Scale and Proportion in Interior Design, helping you strike the ideal balance for a visually pleasing and harmonious home.

